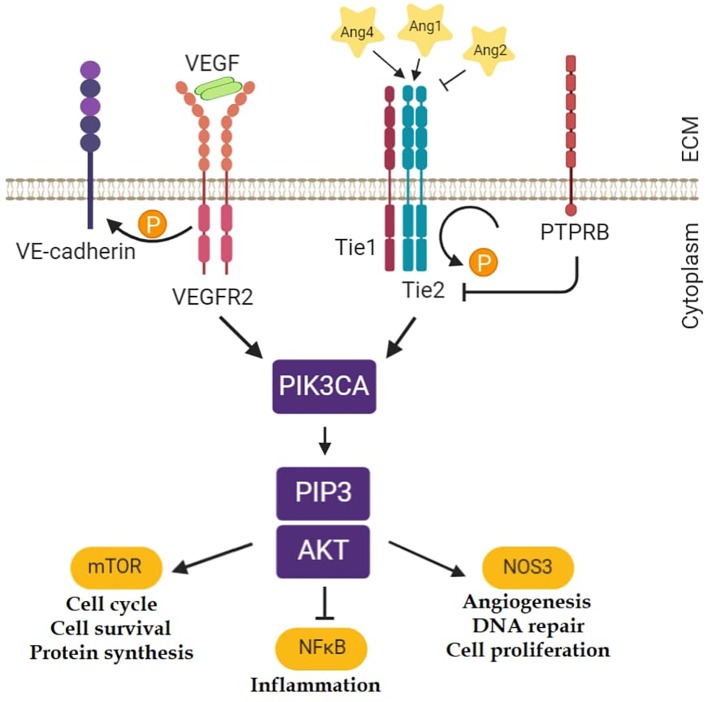
Tie2, coded by the TEK gene, is a tyrosine kinase receptor and performs a central function in vascular stability. It was prompt that variations in the TEK gene may affect the susceptibility to bronchial asthma and allergic conjunctivitis.
The purpose of this research was to additional examine these strategies, involving totally different populations and to check the Tie2 associated pathway on a mouse mannequin of bronchial asthma.
The discovery, stage I cohort concerned 306 sufferers with average and extreme allergic rhinitis, the stage II research consisted of 4 cohorts, specifically, grownup and pediatric asthmatics and corresponding controls. Altogether, there have been 1,258 unrelated people in these cohorts, out of which 63.9% had been kids and 36.1% had been adults.
In stage I, 112 SNPs had been screened in the TEK gene of the sufferers in order to seek for associations with bronchial asthma and allergic conjunctivitis. The prime related SNPs had been chosen for affiliation research on the replication cohorts.
The rs3824410 SNP was nominally related to a diminished danger of bronchial asthma in the stage I cohort and with extreme bronchial asthma inside the asthmatic inhabitants (p=0.009; OR=0.48) in the replication cohort. In the stage I research, 5 SNPs had been chosen in conjunctivitis. Due to the low quantity of grownup sufferers with conjunctivitis, solely kids had been concerned in stage II.
Within the asthmatic kids, the rs622232 SNP was related to conjunctivitis in boys in the dominant mannequin (p=0.004; OR=4.76), whereas the rs7034505 confirmed affiliation to conjunctivitis in women (p=0.012; OR=2.42).
In the lung of a mouse mannequin of bronchial asthma, expression modifications of 10 Tie2 pathway-related genes had been evaluated at three factors in time. Eighty p.c of the chosen genes confirmed vital modifications in their expressions no less than at one time level throughout the course of, main from sensitization to allergic airway irritation.
The expressions of each the Tek gene and its ligands confirmed a diminished degree in any respect time factors. In conclusion, our outcomes present further proof that the Tie2 pathway, the TEK gene and its variations might need a task in bronchial asthma and allergic conjunctivitis. The gene and its related pathways will be potential therapeutic targets in each ailments.

In Vivo Allergen-Activated Eosinophils Promote Collagen I and Fibronectin Gene Expression in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells through TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Asthma.
Eosinophils infiltration and releasing TGF-β1 in the airways has been implicated in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma, particularly throughout acute episodes provoked by an allergen. TGF-β1 is a serious mediator concerned in pro-inflammatory responses and fibrotic tissue transforming in bronchial asthma.
We aimed to guage the impact of in vivo allergen-activated eosinophils on the expression of COL1A1 and FN in ASM cells in bronchial asthma. A complete of 12 allergic bronchial asthma sufferers and 11 wholesome topics had been examined. All research topics underwent bronchial problem with D. pteronyssinus allergen.
Eosinophils from peripheral blood had been remoted earlier than and 24 h after the bronchial allergen problem utilizing high-density centrifugation and magnetic separation. Individual co-cultures of blood eosinophils and immortalized human ASM cells had been ready. The TGF-β1 focus in tradition supernatants was analyzed utilizing ELISA.
Gene expression was analyzed utilizing qRT-PCR. Eosinophils integrins had been suppressed with linear RGDS peptide earlier than co-culture with ASM cells. Results:
The expression of TGF-β1 in asthmatic eosinophils considerably elevated over non-activated asthmatic eosinophils after allergen problem, p < 0.001. The TGF-β1 focus in tradition supernatants was considerably larger in samples with allergen-activated asthmatic eosinophils in comparison with baseline, p < 0.05. The impact of allergen-activated asthmatic eosinophils on the expression of TGF-β1, COL1A1, and FN in ASM cells was extra vital in comparison with non-activated eosinophils, p < 0.05, nevertheless, no distinction was discovered on WNT-5A expression.
The incubation of allergen-activated asthmatic eosinophils with RGDS peptide was more practical in comparison with non-activated eosinophils as the gene expression in ASM cells was downregulated equally to the identical degree as wholesome eosinophils.
